来源:土壤观察
原标题:onmental Science & Technology:全球表层土壤Hg分布状况及其驱动因素
导 读
中科院地球化学研究所冯新斌研究员团队利用稳定Hg同位素分析和地球空间资料,绘制了0~20cm表层土壤中Hg的浓度和全球空间分布图,并对其驱动因素进行了分析。
来源:转载自农业环境科学公号(2019年9月8日)

中科院地球化学研究所冯新斌研究员团队利用稳定Hg同位素分析和地球空间资料,绘制了0~20cm表层土壤中Hg的浓度和全球空间分布图,并对其驱动因素进行了分析。相关成果发表于Environmental Science & Technology(IF=7.149)。
Abstract
Soil is the largest Hg reservoir globally. Data of Hg concentration in surface soil are fundamental to understanding environmental Hg cycling. However, present knowledge on the quantity and global distribution of Hg in soil remains deficient. Using stable Hg isotopic analyses and geospatial data, the concentration and global spatial distribution of Hg in surface soil of 0–20 cm depth have been developed. It is estimated that 1088 ± 379 Gg of Hg is stored in surface soil globally. Thirty-two percent of the surface Hg storage resides in tropical/subtropical forest regions, 23% in temperate/boreal forest regions, 28% in grassland and steppe and shrubland, 7% in tundra, and 10% in desert and xeric shrubland. Evidence from Hg isotopic signatures points to atmospheric Hg0 dry deposition through vegetation uptake as the primary source of Hg in surface soil. Given the influence of changing climate on vegetative development, global climate change can act as an important forcing factor for shaping spatial distribution of Hg in surface soil. This active forcing cycle significantly dilutes the impacts caused by Hg release from anthropogenic sources, and needs to be considered in assessing the effectiveness of reducing Hg use and emissions as specified in Minamata Convention on Mercury.
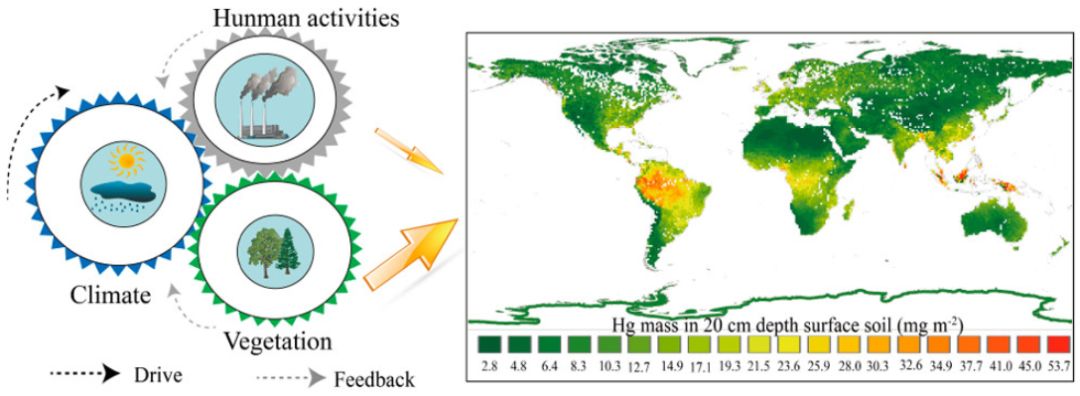
土壤是全球最大的汞(Hg)库。表层土壤中Hg浓度数据是了解环境Hg循环的基础。然而,目前对土壤中Hg的数量和全球分布的认识仍然匮乏。本文利用稳定Hg同位素分析和地球空间资料,绘制了0~20cm表层土壤中Hg的浓度和全球空间分布图,并对其驱动因素进行了分析。研究估计,全球表层土壤中Hg的储量为1088±379 Gg。地球表层土壤Hg储量的32%分布在热带/亚热带森林地区,23%分布在温带/北方森林地区,28%分布在草地、草原及灌丛,7%分布在冻土带,10%分布在沙漠和干旱区灌丛。Hg同位素特征表明,地表土壤中Hg的主要来源是植物吸收引起的大气Hg0干沉降。考虑到气候变化对植物生长发育的影响,全球气候变化可能是地球表层土壤Hg空间分布的重要驱动因素。这种强有力的正反馈循环大幅稀释了人为来源的Hg排放造成的影响,需要在评估《水俣公约》中有关减少Hg使用和排放的规定时加以考虑。
来源:turangguancha 土壤观察
原文链接:http://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzA3MDMwNTExNg==&mid=2659318879&idx=1&sn=3e9b761120a1e9669c9c54c32740a2c2&chksm=844b886cb33c017a3ca1dda006611eae862c3d93f79f38af9943559b87788a8ee8e46ef22e6a&scene=27#wechat_redirect
版权声明:除非特别注明,本站所载内容来源于互联网、微信公众号等公开渠道,不代表本站观点,仅供参考、交流、公益传播之目的。转载的稿件版权归原作者或机构所有,如有侵权,请联系删除。
电话:(010)86409582
邮箱:kejie@scimall.org.cn