来源:中科院大气物理研究所
原标题:【LatestArticles】:厄尔尼诺振幅变化对1990年代末热带太平洋降水减少的贡献

Citation:
Suqi GUO & Renguang WU (2019) Contribution of El Niño amplitude change to tropical Pacific precipitation decline in the late 1990s, Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters, DOI: 10.1080/16742834.2019.1633230

Keywords:
Tropical Pacific precipitation decline, Interdecadal Pacific Oscillation phase switch, interannual SST effect, large-amplitude El Niño events
厄尔尼诺振幅变化对1990年代末热带太平洋降水减少的贡献
中文导读
二十世纪90年代末期,赤道中东太平洋降水显著减少。前人研究多将这个减少归因于太平洋年代际振荡的位相转变,即类拉尼娜型海表温度变化。作者通过一系列大气环流模式实验,揭示了年际海表温度变化对赤道中东太平洋降水减少有很大贡献。这与二十世纪90年代末期厄尔尼诺事件振幅减小有关。1980–1998年代相较于1999–2014年代有更多大振幅厄尔尼诺事件。由于降水对海温异常的非线性响应,使得1980–1998年代相较于1999–2014年代,赤道中东太平洋地区年代平均降水较多。本文结果强调了厄尔尼诺振幅改变在全球变暖背景下未来气候变化中的重要性。
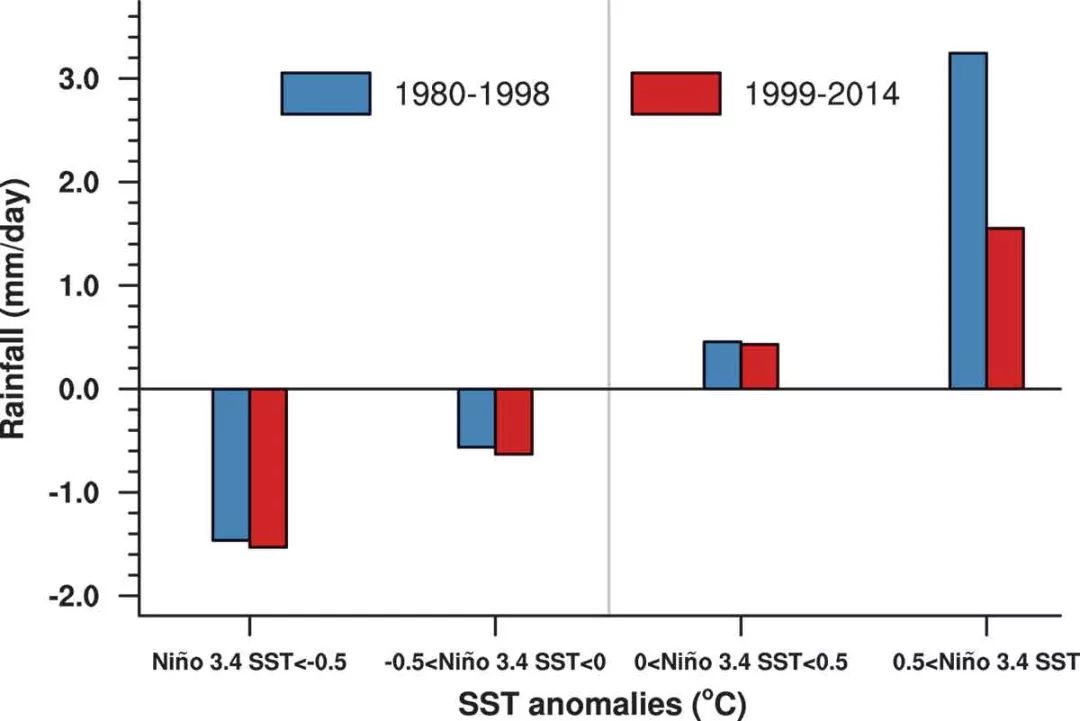
Figure. Area-mean DJF precipitation (units: mm d−1) anomalies during 1980–98 (blue bars) and 1999–2014 (red bars) averaged over the region (10°S–5°N, 170°E–135°W) based on the mean of eight interannual SST simulations when DJF Niño3.4 SST anomalies were below −0.5°C, between −0.5°C and 0°C, between 0°C and +0.5°C, and above +0.5°C.
原文链接:
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/16742834.2019.1633230
来源:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/VBkTH4g-e4a1FECMX7j1qg 中科院大气物理研究所
原文链接:http://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzAxNjM0NTY4MQ==&mid=2654568938&idx=2&sn=ce9abaa11a51400dd966a760409d56f1&chksm=803b1ed4b74c97c282936c27d097b3f23098f5e19c14933baba4fed9babf6ee26b97a2a76452&scene=27#wechat_redirect
版权声明:除非特别注明,本站所载内容来源于互联网、微信公众号等公开渠道,不代表本站观点,仅供参考、交流、公益传播之目的。转载的稿件版权归原作者或机构所有,如有侵权,请联系删除。
电话:(010)86409582
邮箱:kejie@scimall.org.cn